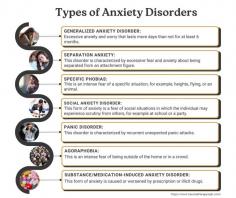
What Is an Anxiety Disorder?
Anxiety disorder, or generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a mental health diagnosis characterized by excessive worry and fear that disrupt behavior. Fear is usually a response to real danger, however, anxiety is irrational fear or anticipation of a future threat. Anxiety can prevent you from doing things you may need to do or enjoy. People with anxiety disorders overestimate the danger of situations, which causes them to avoid sometimes necessary tasks.
Symptoms of anxiety disorder include:
Excessive worry
Difficulty in controlling the worry
Restlessness
Being easily tired
Difficulty concentrating
Irritability
Muscle tension
Sleep disturbance
Anxiety can be useful to alert us of danger and to keep us safe. However, when you begin to experience anxiety related to irrational fears that begin to have negative effects on your life, it becomes a disorder.
Who Is at Risk for Anxiety Disorders?
While anyone may experience anxiety, some risk factors include:
- Family history: Genetics plays a role in anxiety disorders. If someone in your family has a history of anxiety, your risk for anxiety increases.
- Stress: Increased stressful events can increase the risk of anxiety.
- Trauma: The physical and mental changes that occur in the body and mind during a traumatic experience increase the chance of experiencing anxiety.
- Substance use: People tend to experience heightened anxiety when substances wear off or when going through detox.
- Medical conditions: Individuals with medical conditions such as heart disease, respiratory issues, and chronic pain may experience higher anxiety symptoms.
With the help of a therapist, you can learn healthy, quick, and effective coping skills to help you deal with your anxiety.
Read more: https://www.traumatherapywpb.com/conditions/anxiety-disorder/

