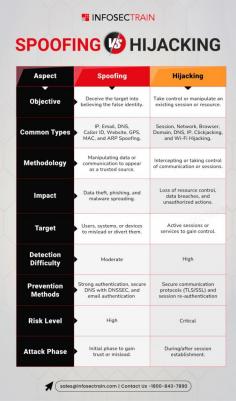
Spoofing and hijacking are two distinct cyberattack techniques used by attackers to exploit systems, though they differ in their methods and objectives. Spoofing involves impersonating a trusted entity to deceive a target into granting access or divulging sensitive information. Common types include email spoofing, IP spoofing, and website spoofing, where attackers disguise their identity to appear legitimate. In contrast, hijacking refers to taking over a legitimate session or connection, such as session hijacking or browser hijacking, where an attacker intercepts and controls an active communication channel. While spoofing focuses on deception and masquerading, hijacking emphasizes unauthorized control and exploitation. Both attacks pose significant risks to individuals and organizations, highlighting the importance of robust authentication mechanisms, encryption, and proactive monitoring to defend against these threats.

